 |
 |
Gregor Mendel’s theories of inheritance are published. |
 |
|
Friedrich Miescher isolates and identifies nuclein (later known as DNA). |
 |
|
Walther Flemming discovers chromosomes. |
 |
|
Theodor Boveri and Walter Sutton propose that chromosomes
are responsible for heredity. |
 |
|
Archibald Garrod proposes that some diseases result from changes in "genetic factors," now known as genes. |
 |
|
Wilhelm Johannsen coins the term "gene." |
 |
|
Thomas Morgan Hunt shows that genes, which exist on chromosomes, are the basic units of inheritance. |
 |
|
Han Winkler coins the term "genome" to refer to all the genes in an organism. |
 |
|
George Beadle and Edward Tatum show that genes control the functions of a cell because each gene codes for a protein. |
 |
|
Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty provide evidence that DNA, one of the primary components of chromosomes and genes, is the chemical substance responsible for inheritance. |
 |
|
Erwin Chargaff provides important statistical clues to the structure of DNA. |
 |
|
Rosalind Franklin produces "Photo 51," which is crucial in helping to decipher the structure of DNA |
 |
|
James Watson and Francis Crick discover the double helix structure of DNA. |
 |
|
Marshall Nirenberg cracks the genetic code, which is the code of inheritance. |
 |
|
A company called Genentech creates a breakthrough treatment for diabetes by genetically engineering bacteria to produce human insulin that can be purified and given to humans as a substitute for their own insulin. This is the first drug made through the use of genetic engineering. |
 |
|
With blood samples collected from a large family in Venezuela, scientists identify the gene responsible for Huntington’s disease, leading to the first genetic test for a disease. |
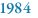 |
|
Sir Alec John Jeffreys develops DNA profiling (also known as DNA fingerprinting) to be used in forensics, paternity, and immigration cases. |
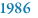 |
|
Richard Buckland becomes the first person acquitted of a crime
based on DNA evidence. |
 |
|
Colin Pitchfork becomes the first murderer identified by DNA evidence after raping and murdering two schoolgirls, the same crime Richard Buckland was acquitted of the previous year. |
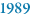 |
|
Stephen Fodor builds the first specialized DNA "microarray," which would lead to a cost-effective method of testing for hundreds of thousands of genetic variants at once. |
 |
|
The Human Genome Project is launched. |
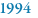 |
|
Scientists locate the BRCA1 gene, responsible for almost half of all
early-onset breast cancer and the majority of breast and ovarian cancers
that run in families. |
 |
|
Researchers at Scotland’s Roslin Institute report cloning a sheep
they name Dolly. In that same year a movie called Gattaca (whose name contains only the four chemical letters found in DNA) depicts a future in which genetic information has been fully integrated into, and is utilized by, all segments of society.
|